High-performance/pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a chromatographic method that is used to separate a mixture of compounds in analytical chemistry and biochemistry so as to identify, quantify or purify the individual components of the mixture.
More information about HPLC.
Video about HPLC.

The time inside the column depends only on the structure, polarity and molecular weight of the compound.
Chromatography is a technique for the separation of a mixture by passing it in solution or suspension through a medium in which the components move at different rates.
Is a method used to isolate a single chemical compound from a mixture. This can be done using gravity to move the solvent, or using compressed gas to push the solvent through the column.
Molecular docking is a molecular modeling technique that is used to predict how a protein (enzyme) interacts with small molecules (ligands).
This is useful for predicting both the strength and type of signal produced. Molecular docking is one of the most frequently used methods in structure-based drug design, due to its ability to predict the binding-conformation of small molecule ligands to the appropriate target binding site.
A protein is a group of many amino acids together, which are divided into an amino group and an acid group, the only thing that varies is the R group (side chain). In group R there are 20 different types of amino acids.
To build proteins, cells use a complex assembly of molecules called a ribosome. The ribosome assembles amino acids into the proper order and links them together via peptide bonds. This process, known as translation, creates a long string of amino acids called a polypeptide chain.
Polar amino acids are those with side-chains that prefer to reside in an aqueous (water) environment. For this reason, one generally finds these amino acids exposed on the surface of a protein.
ACE2 means Angiotensin-converting enzyme type 2
The tail movement model is an animal model for the evaluation of analgesic activity in rats or mice. Method based on the simple principle, since the tail of the mice comes into contact with the heat, it will try to remove the tail or move it from the source of stimuli. It shows the normal reaction time for pain perception and is considered the end point. This behavior is also applicable to humans. After the rat wags its tail, they are treated with analgesic medication and then their response time is again noted. If that drug has analgesic property, there will be a delay in response time. Generally, rats show a response in 3 to 5 seconds, if it takes more than 10 to 12 seconds, the rats will eliminate from the experiments to avoid further damage.
Video about Tail Flick method.
Xuebijing injection (XBJ) is one of the therapeutic drugs recommended in the practice guidelines published by the Chinese Health Commission. Few clinical studies on the treatment of COVID-19 by XBJ have been found. Xuebijing is a mixture of 4-5 herbal drugs.
XBJ is an important form of therapy in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). XBJ consists of Carthamus tinctorius, Radix Paeoniae Rubra, Ligusticum wallichii, Salvia miltiorrhiza, and Angelica sinensis.
More information about Xuebijing injection.

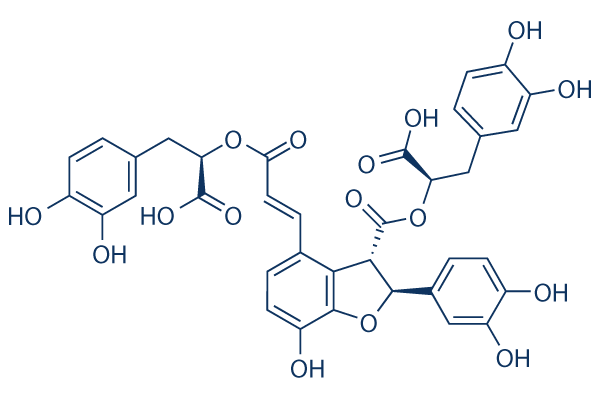
Salvianolic acid B (Sal B, Lithospermate B, Lithospermic acid B), an antioxidant and free radical scavenging compound, is the most abundant bioactive compound extracted from the root of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge.
- Molecular Formula: C36H30O16
- Molecular weight: 718.6
More information about Salvianolic acid B.